Malware string hash lookup plugin for IDA Pro. This plugin connects to the OALABS HashDB Lookup Service.
The hash algorithm database is open source and new algorithms can be added on GitHub here. Pull requests are mostly automated and as long as our automated tests pass the new algorithm will be usable on HashDB within minutes.
Using HashDB
HashDB can be used to look up strings that have been hashed in malware by right-clicking on the hash constant in the IDA disassembly view and launching the HashDB Lookup client.
Settings
Before the plugin can be used to look up hashes the HashDB settings must be configured. The settings window can be launched from the plugins menu Edit->Plugins->HashDB.
Hash Algorithms
Click Refresh Algorithms to pull a list of supported hash algorithms from the HashDB API, then select the algorithm used in the malware you are analyzing.
Optional XOR
There is also an option to enable XOR with each hash value as this is a common technique used by malware authors to further obfuscate hashes.
API URL
The default API URL for the HashDB Lookup Service is https://hashdb.openanalysis.net/. If you are using your own internal server this URL can be changed to point to your server.
Enum Name
When a new hash is identified by HashDB the hash and its associated string are added to an enum in IDA. This enum can then be used to convert hash constants in IDA to their corresponding enum name. The enum name is configurable from the settings in the event that there is a conflict with an existing enum.
Hash Lookup
Once the plugin settings have been configured you can right-click on any constant in the IDA disassembly window and look up the constant as a hash. The right-click also provides a quick way to set the XOR value if needed.
Bulk Import
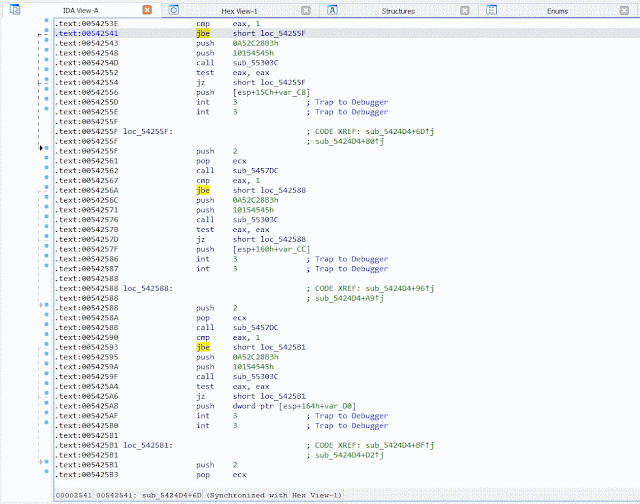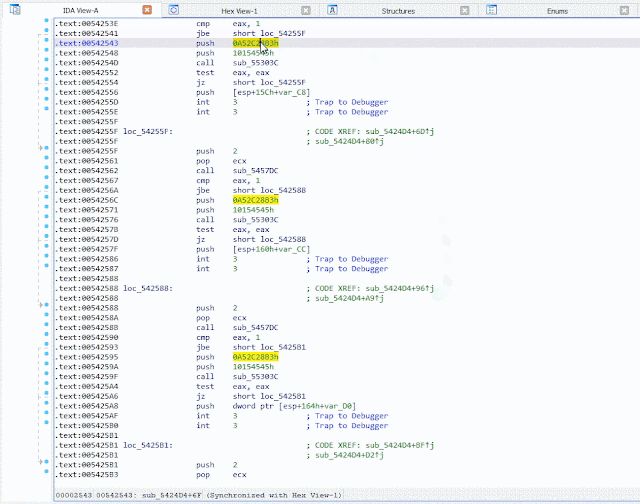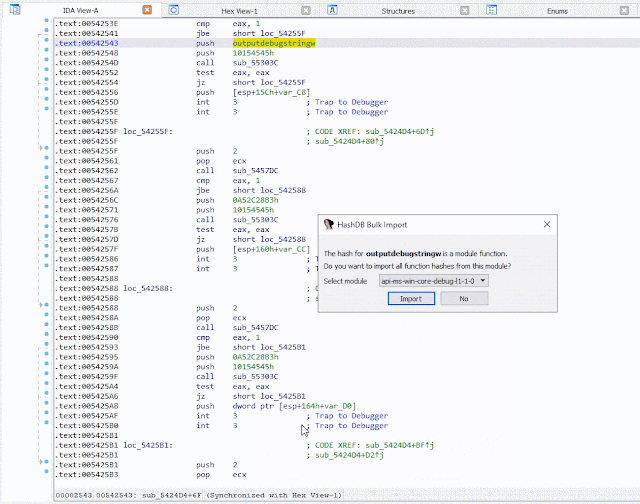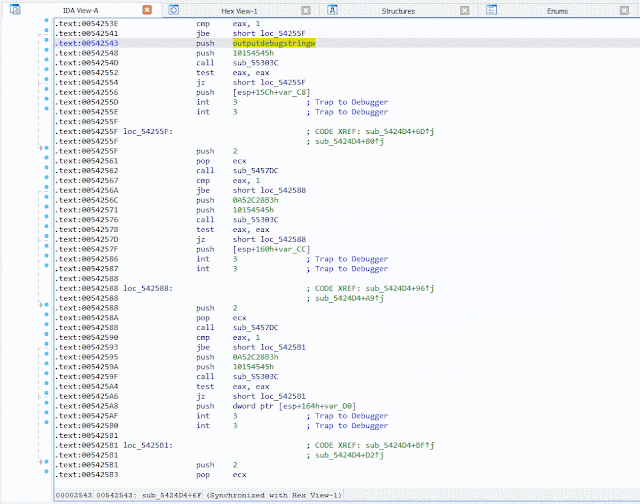
If a hash is part of a module a prompt will ask if you want to import all the hashes from that module. This is a quick way to pull hashes in bulk. For example, if one of the hashes identified is Sleep from the kernel32 module, HashDB can then pull all the hashed exports from kernel32.
Algorithm Search
HashDB also includes a basic algorithm search that will attempt to identify the hash algorithm based on a hash value. The search will return all algorithms that contain the hash value, it is up to the analyst to decide which (if any) algorithm is correct. To use this functionality right-click on the hash constant and select HashDB Hunt Algorithm.
All algorithms that contain this hash will be displayed in a chooser box. The chooser box can be used to directly select the algorithm for HashDB to use. If Cancel is selected no algorithm will be selected.
Instead of resolving API hashes individually (inline in code) some malware developers will create a block of import hashes in memory. These hashes are then all resolved within a single function creating a dynamic import address table which is later referenced in the code. In these scenarios the HashDB Scan IAT function can be used.
Simply select the import hash block, right-click and choose HashDB Scan IAT. HashDB will attempt to resolve each individual integer type (DWORD/QWORD) in the selected range.
Installing HashDB
Before using the plugin you must install the python requests module in your IDA environment. The simplest way to do this is to use pip from a shell outside of IDA.
pip install requests
Once you have the requests module installed simply copy the latest release of hashdb.py into your IDA plugins directory and you are ready to start looking up hashes!
The HashDB plugin has been developed for use with the IDA 7+ and Python 3 it is not backwards compatible.
More info
- Hacker Hardware Tools
- Pentest Tools For Mac
- Hacking Tools Software
- Pentest Tools Kali Linux
- Tools 4 Hack
- Pentest Reporting Tools
- Hackers Toolbox
- Pentest Recon Tools
- Hacker Tools Github
- World No 1 Hacker Software
- Hack Tools
- Hacker Tools For Ios
- Hacking Tools For Windows 7
- Hacker Tools For Pc
- Hack Apps
- Physical Pentest Tools
- Hacker Tools Online
- Hacking Tools Usb
- Usb Pentest Tools
- Hacker Tools Hardware
- Hacking Tools For Mac
- Pentest Tools Apk
- Hacking Tools Software
- Pentest Tools Subdomain
- Hacker
- Blackhat Hacker Tools
- Android Hack Tools Github
- Pentest Tools Online
- Pentest Tools Url Fuzzer
- Hack Tools
- Black Hat Hacker Tools
- Hacking Tools Windows
- Hacking Tools For Beginners
- Hacker Security Tools
- Tools For Hacker
- Free Pentest Tools For Windows
- Hak5 Tools
- Github Hacking Tools
- Hacking Tools For Windows
- Hack Tools Mac
- Hacking Tools Windows 10
- Bluetooth Hacking Tools Kali
- Pentest Automation Tools
- Hacking Tools For Windows 7
- Pentest Tools For Mac
- Hacker Tools For Pc
- Hacker Tools For Pc
- Hacking Tools For Beginners
- Hacking Tools Mac
- Hack Tools
- Pentest Tools Review
- Black Hat Hacker Tools
- Hack Tool Apk No Root
- Hacking Tools And Software
- Hacking Tools Usb
- Hacker Tools Online
- Pentest Box Tools Download
- Hacking Tools For Beginners
- Hacking Tools For Kali Linux
- Hacking Tools For Pc
- Hacking Tools Download
- Hacking Tools Free Download
- Pentest Tools Online
- Pentest Tools For Mac
- Hacking Tools Pc
- Pentest Tools For Android
- Hacking Tools Online
- Android Hack Tools Github
- Wifi Hacker Tools For Windows
- Hacker Tools Linux
- Hack Tools For Windows
- Pentest Tools Subdomain
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Pentest Box Tools Download
- Hacker Tools Online
- Termux Hacking Tools 2019
- Hack Website Online Tool
- Hacking Tools For Windows
- Game Hacking
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- How To Make Hacking Tools
- Pentest Tools List
- Hacker Tools For Pc
- Best Hacking Tools 2019
- Hacking Tools Mac
- Pentest Tools Free
- Pentest Tools Review
- Hack Tool Apk No Root
- Pentest Tools Windows
- Hack App
- Hacker Techniques Tools And Incident Handling
- Hacking Tools Pc
- Hacking Tools Usb
- Hacking Tools Mac
- Hack Tool Apk No Root
- Hack App
- Hacker Tools For Windows
- Nsa Hacker Tools
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Hacker Search Tools
- New Hack Tools
- Hacker Security Tools
- Pentest Tools Nmap
- Hacker Tools Github
- Hack Website Online Tool
- Black Hat Hacker Tools
- Nsa Hack Tools
- Tools Used For Hacking
- Beginner Hacker Tools
- Best Pentesting Tools 2018
- Hacker Tools 2020
- Hack Tools
- Hacker Tools Github
- New Hacker Tools
- Hack App
- What Is Hacking Tools
- Bluetooth Hacking Tools Kali
- Hacking Tools Usb
- Hacker Tools Github
- Hacker Tools Windows
- Hack Rom Tools
- Pentest Tools Windows
- Pentest Tools Review